Anxiety and weight loss are two topics that often go hand in hand. While anxiety can be a contributing factor to weight gain, it can also be a barrier to achieving weight loss goals. In this article, we will explore the link between anxiety and weight loss, including the ways in which anxiety can impact weight, the potential consequences of this relationship, and strategies for managing anxiety to support weight loss efforts.
What is anxiety?
Anxiety is a normal and natural part of life. It is a feeling of nervousness or worry about something that may or may not happen in the future. Everyone experiences anxiety at some point in their lives, and it is a common response to stress or uncertainty.
However, when anxiety becomes excessive or persistent, it can interfere with daily life and become a disorder. According to the National Institute of Mental Health, anxiety disorders are the most common mental illness in the United States, affecting about 40 million adults (18% of the population).
There are several different types of anxiety disorders, including generalized anxiety disorder, panic disorder, phobias, social anxiety disorder, and obsessive-compulsive disorder. Symptoms of anxiety disorders can include racing thoughts, difficulty concentrating, irritability, sleep disturbances, and physical symptoms such as muscle tension and rapid heartbeat.
How anxiety impacts weight
Anxiety can impact weight in a number of ways. For some people, anxiety may lead to weight gain due to unhealthy coping mechanisms such as emotional eating or avoidance of physical activity. Others may experience weight loss as a result of anxiety due to decreased appetite or excessive exercise as a means of coping.
Emotional eating
Emotional eating is a common coping mechanism for people with anxiety. When we feel anxious or stressed, we may turn to food as a source of comfort or distraction. This can lead to overeating or choosing unhealthy foods that provide temporary relief but do not address the underlying cause of the anxiety.
Physical inactivity
Anxiety can also lead to decreased physical activity due to avoidance of situations or activities that trigger anxiety symptoms. This can result in weight gain due to decreased calorie expenditure. Additionally, anxiety can cause physical symptoms such as fatigue, which can further reduce motivation for physical activity.
Decreased appetite
Anxiety can also lead to weight loss due to decreased appetite. Some people with anxiety may experience stomachaches, nausea, or other digestive issues that make eating difficult. Others may simply lose their appetite due to the mental and physical demands of managing anxiety.
Excessive exercise
While exercise is generally beneficial for physical and mental health, excessive exercise can be a coping mechanism for people with anxiety. This may involve over-exercising to the point of exhaustion or neglecting other important aspects of self-care such as sleep or nutrition.
Consequences of the anxiety-weight relationship
The link between anxiety and weight can have serious consequences for both physical and mental health.
Physical health consequences
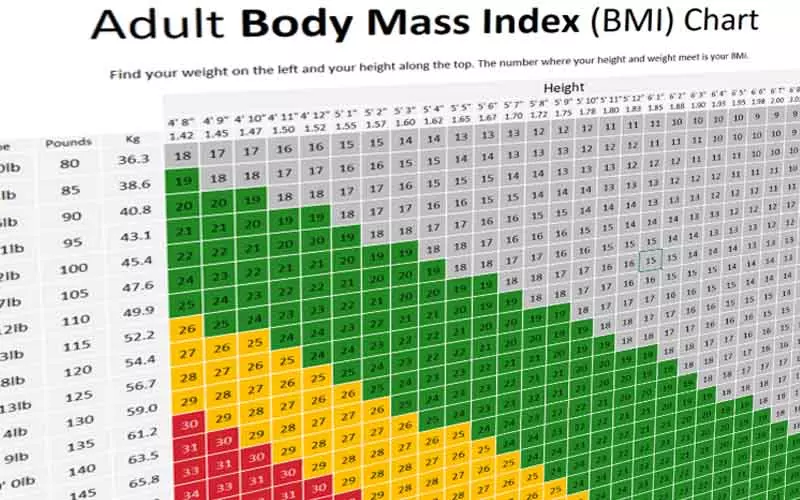
Weight gain or loss due to anxiety can have significant impacts on physical health. Excessive weight gain can increase the risk of obesity and related health problems such as diabetes, heart disease, and high blood pressure. Weight loss due to anxiety may also result in malnutrition and other health problems related to inadequate nutrition.
Mental health consequences
Anxiety and weight struggles can also have negative impacts on mental health. The stress and frustration of trying to lose weight or maintain a healthy weight may exacerbate anxiety symptoms or lead to the development of other mental health conditions such as depression. Additionally, the negative self-image and body dissatisfaction that can result from weight struggles can contribute to low self-esteem and self-worth.
Managing anxiety to support weight loss efforts
Here are some tips for managing anxiety:
- Seek professional help: If your anxiety is severe or disrupting your daily life, it is important to seek help from a mental health professional. A therapist or counselor can help you identify the underlying causes of your anxiety and develop coping strategies to manage it.
- Practice self-care: Self-care is crucial for managing anxiety. This can include activities such as regular exercise, getting enough sleep, eating a healthy diet, and finding time for relaxation and enjoyable activities.
- Use relaxation techniques: Relaxation techniques such as deep breathing, progressive muscle relaxation, and mindfulness meditation can help reduce anxiety and promote feelings of calm. These techniques can be particularly helpful in managing anxiety triggers related to food and exercise.
- Set achievable goals: Setting realistic and achievable goals is important for managing anxiety. Rather than trying to make sweeping changes all at once, try setting small, achievable goals that you can work towards over time. This can help you build momentum and feel a sense of accomplishment as you progress.
- Seek support: It can be helpful to seek support from friends, family, or a support group as you work towards your anxiety management goals. Having a supportive network can provide encouragement and accountability, as well as a sense of community and belonging.
- Practice stress-reducing activities: Engaging in activities such as yoga, meditation, or tai chi can help reduce anxiety and improve overall health.
- Seek help for any underlying medical conditions: If you have any underlying medical conditions that may be contributing to your anxiety, it is important to seek help and address these issues.
- Practice gratitude: Focusing on the positive aspects of your life and practicing gratitude can help reduce anxiety and improve overall well-being.
- Create a daily routine: Having a daily routine and sticking to it can help reduce uncertainty and anxiety.
- Limit caffeine and alcohol: Caffeine and alcohol can exacerbate anxiety symptoms, so it is important to limit or avoid these substances.
- Get enough sunlight and fresh air: Getting enough sunlight and fresh air can help regulate your mood and reduce anxiety.
- Practice good sleep hygiene: Creating a relaxing bedtime routine and avoiding screens before sleep can help improve your sleep and reduce anxiety.
- Use positive self-talk: Using positive affirmations and self-talk can help challenge negative thoughts and beliefs that contribute to anxiety.
- Practice mindfulness: Focusing on the present moment rather than worrying about the future can help reduce anxiety and increase overall well-being.
- Find healthy ways to cope with stress: Rather than turning to unhealthy coping mechanisms such as emotional eating or avoidance, try finding healthy ways to cope with stress such as talking to a friend or writing in a journal.
- Seek support from a support group: Joining a support group or online community for people with anxiety can provide a sense of community and belonging, as well as support and guidance.
- Consider natural remedies: Natural remedies such as herbs or supplements may be helpful for managing anxiety. It is important to talk to a healthcare professional before trying any new treatment.
- Take breaks and set boundaries: Taking breaks and setting boundaries can help prevent overwhelming yourself with tasks and responsibilities, which can contribute to anxiety.
- Seek help for co-occurring mental health conditions: If you have any co-occurring mental health conditions
Conclusion
Anxiety and weight loss are interconnected issues that can have significant impacts on both physical and mental health. While anxiety can be a barrier to achieving weight loss goals, it is possible to manage anxiety and support weight loss efforts by seeking professional help, practicing self-care, using relaxation techniques, setting achievable goals, and seeking support. By addressing both anxiety and weight loss in a holistic manner, you can take steps towards improving your overall health and well-being.
Photo by Luiz Rogério Nunes on Unsplash